Frontal Sinus Osteoma Right, Left, Complications, Treatment
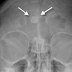
The frontal sinus is where osteomas, benign tumor of the paranasal sinuses and nose, most frequently occur. This tumor is detected inadvertently on radiography, or it grows to the point where it causes symptoms and, on occasion, consequences that are related to its placement close to the orbit and the front cranial vault. Osteoma of the frontal sinus refers to a bone formation that resembles a tumor and takes place in the cranial cavity.
Most of the time, the growth is on one side and near the cranial sutures. For example, an osteoma of the left frontal sinus or an osteoma of the right frontal sinus. This type of osteoma is known as a spongy or spongy frontal sinus osteoma if the formation is made up of a spongy (diploid) bone component along with an aggregation of fibrous tissue and adipose tissue components. A mixed osteoma might also exist. The structure growing intracranially on the back wall of the left frontal sinus or the inner side of the left frontal bone is an osteoma of the basal parts of the left frontal sinus or the right frontal sinus.
Frontal Sinus Osteoma Complications
Even though it is rare for an osteoma to grow into the part of the skull that holds the brain, the bigger it is, the more likely it is that it will cause serious problems by applying stress on the frontal lobe of the brain and irritating components of the motor cortex, the frontal oculomotor field, and other structures. Convulsions, disturbed motor coordination, and psychogenic problems can result from this.
The majority of the time, the symptoms of an osteoma that is located nearer to the nasal cavity include trouble in nasal breathing as well as worsening drainage in one or more of the paranasal sinuses, which can ultimately lead to chronic sinusitis. Frontal sinus osteomas' posterior expansion may result in intracranial involvement, and if the dural tissue is penetrated, complications including cerebrospinal fluid fistula, meningitis, pneumocephalus, or frontal abscess may happen.

Frontal Sinus Osteoma Treatment
Osteomas of the paranasal sinuses are uncommon, slow-growing benign lesions with the potential for significant consequences. Frontal sinus osteomas can be surgically removed using a variety of techniques, including the external frontoethmoidal approach and the osteoplastic frontal sinusectomy, both of which have high recurrence rates. Because of the nature of this tumor, typical surgical treatments are not able to completely remove it.
Surgical resection is the primary therapeutic option for osteomas of the sphenoid and ethmoid sinuses, as well as for additional symptoms they cause. Asymptomatic lesions require regular radiographic monitoring. Both the location of the tumor and its size play a role in the method of surgical excision that is chosen. The best ways to treat this disease with drugs have not been found yet, and small frontal sinus osteomas aren't treated unless they cause symptoms. If during the course of diagnostic procedures, a bone osteoma is found but there are no indications that surgical treatment is necessary, then conservative therapy is mostly recommended.
 Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
August 14, 2022
Rating:
Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
August 14, 2022
Rating:











